SOQL Query
SOQL is a Salesforce Object Query Language that allows you to fetch data from Salesforce databases. Understanding of how to use SOQL effectively help to manage data effectively.
What is SOQL?
SOQL is a salesforce specific query language. It is a read only language used for data retrieval only, it cannot be used to modify data. SOQL can help us to achieve
- Retrieve data from salesforce objects or custom objects
- Perform complex queries to filter, sort and organize data
- Retrieve data that meets certain conditions using operators
- Use functions to perform calculations and manipulate data.
Syntax
SELECT fieldApiName1, fieldApiName1, ... FROM objectApiName WHERE filterCondition ORDER BY fieldApiName
SELECT: Specifies the fields or columns you want to retrieve.FROM: Name of object or table from which you want to retrieve data.WHERE(Optional): Filters data on basis of condition, you can club two or more conditions using logical operatorsANDorOR.ORDER BY(Optional): Sort retrieved results on basis of specified fields.
WHERE Clause in SOQL query
WHERE clause allows you to specify conditions that expected results must follow. You can use various operators like LIKE, IN, >, <, =, !=, AND and OR
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry FROM Account WHERE Type != 'Customer - Direct' AND Industry != 'Energy'
In the above example we are retrieving data from Account object where Type is not Customer – Direct and Industry is not energy.
IN Operator
IN operator allows you to check whether field’s value is equal to any of the several possibilities.
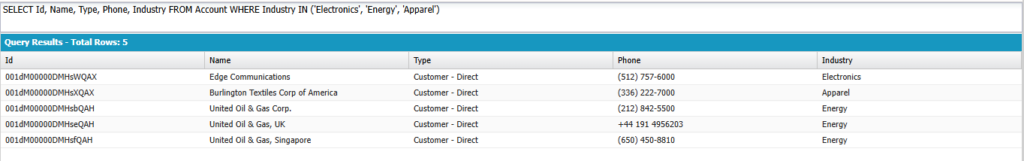
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry
FROM Account
WHERE Industry IN ('Electronics', 'Energy', 'Apparel')
Output
NOT IN operator allows you to exclude records that match a certain set of values.
LIKE Operator
LIKE is particularly useful when you need to search for records based on partial matches. It supports wildcards to help you search for records that match part of string rather than exact value.
%: Represents zero or more characters_: Represents a single character
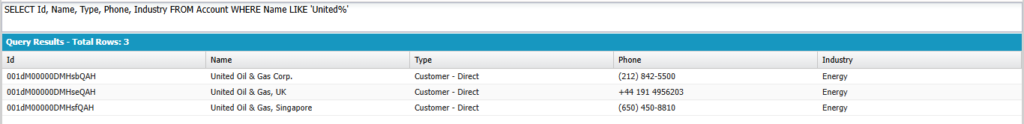
Name starts with ‘United’.
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry FROM Account WHERE Name LIKE 'United%'
Output
Name ends with ‘plc’.
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry FROM Account WHERE Name LIKE '%plc'
Output

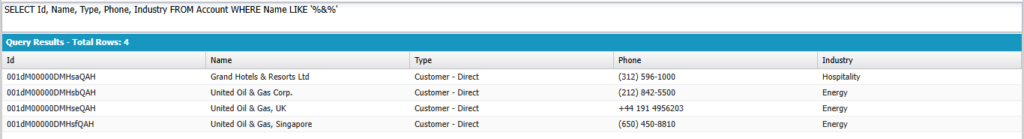
Name contains ‘&’ in it
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry FROM Account WHERE Name LIKE '%&%'
Output
INCLUDES Operator
The INCLUDES operator is useful when you need to check whether multi-select picklist field contains a specific value or set of values.
Accounts in which one of the Language is Hindi or Spanish or both
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry, Language__c
FROM Account
WHERE Language__c INCLUDES ('Hindi','Spanish')
Output

ORDER BY Clause in SOQL query
The ORDER BY clause sorts your result set based on the specified fields either in ascending (default) or descending order
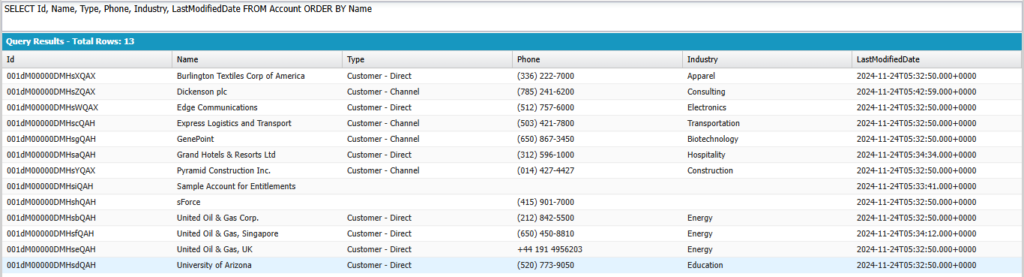
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry, LastModifiedDate FROM Account ORDER BY Name
Output
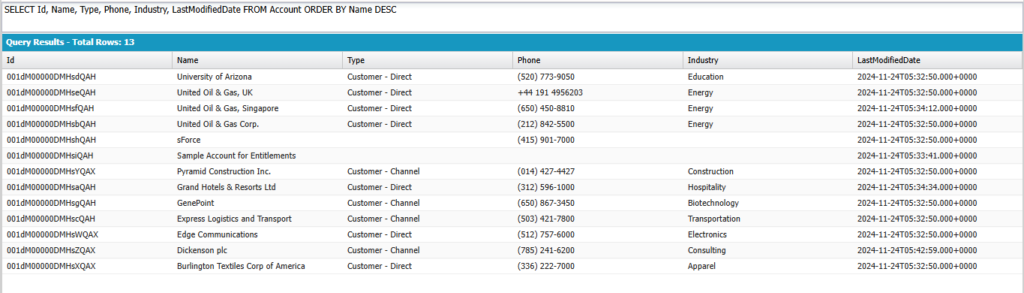
Sort Results by Name in descending order
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry, LastModifiedDate FROM Account ORDER BY Name DESC
Output
LIMIT and OFFSET
LIMIT in SOQL query
LIMIT clause allow you to control the number of results retrieved by the query. This feature useful especially for optimizing performance and managing the volume of data processed in single query statement. You can anytime club LIMIT clause with WHERE and ORDER BY clause.
Syntax
SELECT fieldApiName1, fieldApiName1, ... FROM objectApiName WHERE filterCondition ORDER BY fieldApiName LIMIT Number
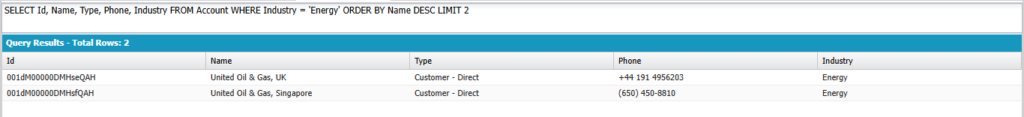
Retrieve two records with Industry as Energy and sort result by name in descending order
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry FROM Account WHERE Industry = 'Energy' ORDER BY Name DESC LIMIT 2
OFFSET in SOQL query
OFFSET clause control starting point of retrieved results in a query. This feature is useful in paginating results.
Syntax
SELECT fieldApiName1, fieldApiName1, ... FROM objectApiName WHERE filterCondition ORDER BY fieldApiName LIMIT OffsetNumber
Skipping the first 5 records
SELECT Id, Name, Type, Phone, Industry FROM Account ORDER BY Name DESC OFFSET 5
Output

Mastering SOQL queries is crucial for efficient salesforce data handling. From simple data retrieval to complex aggregations and relationship queries, SOQL provides powerful tools to explore and manage Salesforce data.